Q&A Chatbots (RAG + Agents)
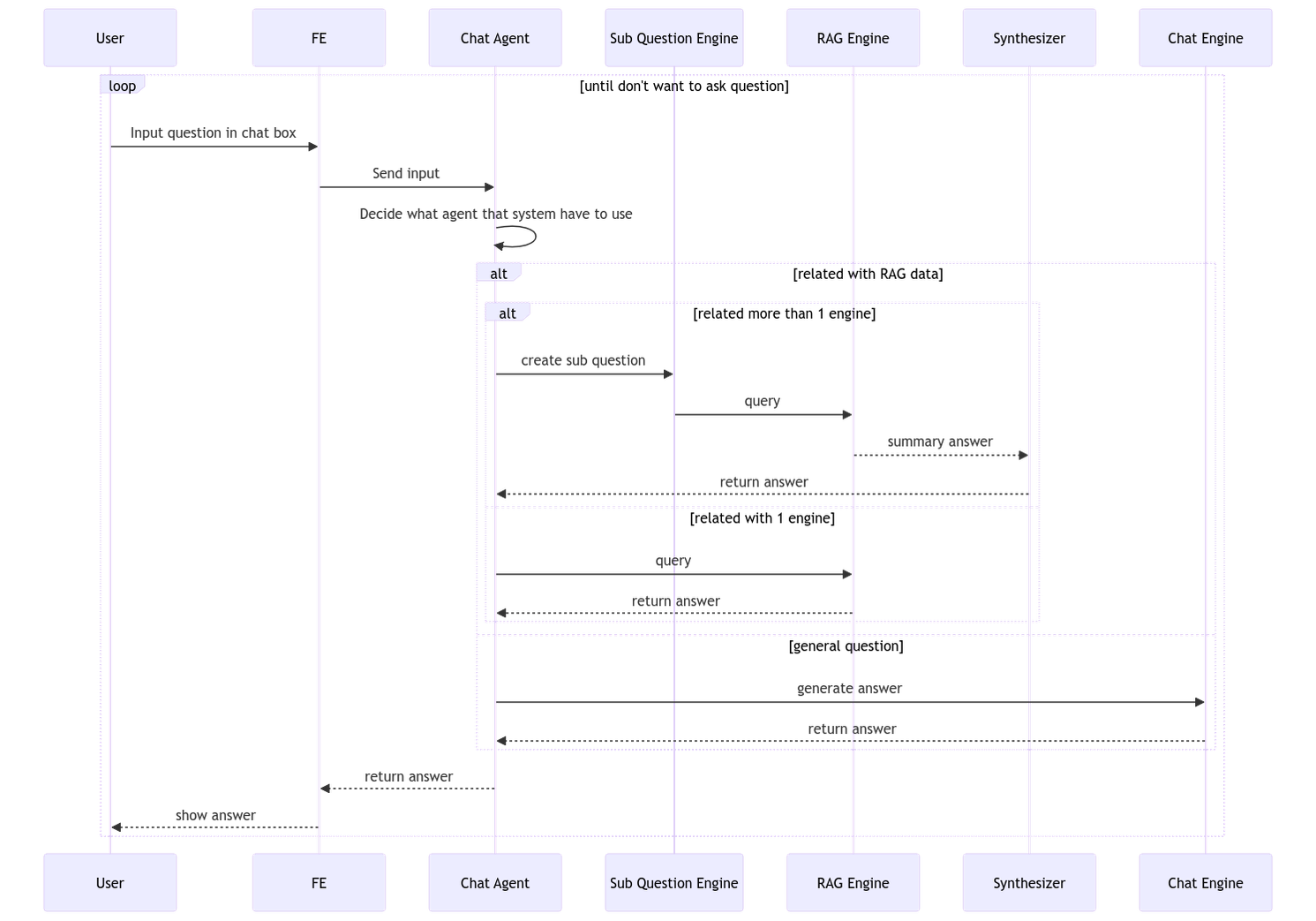
We have developed a Chatbot consisting of two AI agents and an RAG. When a user asks a question to the Chatbot, AI Agent 1 decides whether to use RAG to search for specific information or use LLMs to answer the question. The Chatbot also includes memory that can remember previous responses, making the interaction smoother.
For example, in the RAG demo, we used metadata containing annual performance data from 2019 to 2022 from Uber. If the user asks a question related to the RAG data, AI Agent 1 decides whether to use RAG or answer the question using OpenAI Agent, depending on the relevance.
In this Chatbot implementation, several engines work together, each serving a different purpose. Let's break down each part:
Chat Agent
The Chat Agent uses OpenAI as LLMs and consists of Chat Engine, Sub Question Engine, and RAG Engine. When a user asks a question, the Chat Agent decides whether to answer using RAG or Chat Engine based on the relevance to the RAG metadata description.
Sub Question Engine
If RAG is chosen for answering a question, and the prompt requires data from multiple RAG engines, the question is sent to the Sub Question Engine first. It helps break down the question before sending it to the RAG Engine, which is essential since RAG is divided into four sub-engines, each responsible for answering questions related to specific aspects.
RAG Engine
The RAG Engine uses performance data from Uber for the years 2019 to 2022. The Chat Agent decides whether to send the question directly to RAG or pass it through the Sub Question Engine based on the relevance to the RAG metadata description.
Chat Engine
The Chat Engine, or GPT Engine, answers general questions. When the Chat Agent concludes that the prompt is not related to RAG, it sends the question to the Chat Engine for a general response.
Other
This Chatbot stores conversation data in memory, allowing for smoother interaction by maintaining context.
To reset the chat or clear the memory, the /resetChat command can be used.
The /chat endpoint is used for normal queries, while /chatWithoutRAG can be used for queries without involving RAG.
User Flow
Frontend Development
User Interface Components
The UI components will mainly consist of:
Chat header: Contains settings for the chat and a button to reset the chat.
Chat input: Input for typing and sending messages.
Chat widget: Displays the conversation.
Step 1: Define Schema and Form
In this step, we will use the library react-hook-form, @hookform/resolvers/zod, and 'zod'.
In the first step, we will create a schema.
The schema consists of a query for input and a bot to display error messages for the bot itself.
Once we create the schema, we will create a type interface for this form.
After that, we will create methods.
From the schema itself, we will validate the input received from the user. If the user submits without typing, an error message will be displayed in the user interface saying 'Please enter your message.'
In the input component, the 'react-hook-form' library is used, along with useFormContext and Controller to manage the input.
In the part where the input is called, we will set the attribute name to be 'query,' similar to the variable declared in that schema.
Once we submit, if the input is validated correctly, we will see the data we logged from the onSubmit function, which we can then connect to the backend.
Step 2: Connect Backend
We will set the default base URL.
After setting it up, we will connect to the API.
When we try to submit the form, we will get the value from the API
We will then connect the obtained data to the UI of the Chatbot using React and State Management.
We will use useState from React for state management of messages to display in the UI. We will have answer and setAnswer to store the questions and answers of the user and bot. The structure of the array will be as follows:
We will also manage state for shooting the API. When we ask, we can choose whether to use RAG or not. We will have hasRag and setHasRag to manage the state, allowing us to use this value to check before sending the API to decide which one to shoot.
Step 3: Handle Form Submission
In this step, we handle various states such as loading, submitting, and errors. We use state from 'useFormContext' to display values related to the form, including isSubmitting and errors.
In the ChatWindow component, we manage various states to display in the UI, including loading, submitting, and error states.
Backend Development
Setting Up a FastAPI Project
Similar to all the previous examples, we choose to use FastAPI as the framework to build an API for our application.
First, install the necessary Python libraries for FastAPI:
Create a file named app.py and initialize FastAPI:
In the code above, we initialize a FastAPI project and enable CORS for smooth communication with the frontend. To run the server, use the following command:
This command instructs FastAPI to execute the application defined in the app.py file, and the server will run on the default port 8000.
Next, create the data and storage folders to store sample documents and the vector database storage.
Preparation and Ingest Data
To begin, set up the environment and OpenAI key:
Continue by loading data into the VectorDB. The example uses data from raw UBER 10-K HTML files for the years 2019-2022:
Now, load the data as documents into the VectorDB, organizing it by year:
Setting Up a Sub Question Query Engine
Create a Query Engine for each year's data by loading the index from the VectorDB:
Generate Query Engine Tools for each year's data:
Synthesize Answers Across the Data
Create a function to synthesize questions for individual query engine tools:
Generate a Query Engine Tool for sub-question query engine:
Create General Engine
The final engine we are going to create will serve as a query tool used to search for information that is not within the scope of the prepared data. Alternatively, it can be referred to as a chatbot for answering general questions.
Create OpenAI Agent from Tools
Combine all query engine tools into an OpenAI Agent:
Create RAG API
Build an endpoint for loading data into VectorDB:
Create Chat Endpoint API
Implement an endpoint for processing chat queries:
Create Utility Endpoint
Implement two additional APIs for utility purposes:
Reset the Agent data:
Use a chatbot without RAG:
Deploying and Monitoring on EC2
To deploy FastAPI on an EC2 instance:
Create a session using
screen:Navigate to the API folder:
Start FastAPI on port 8000:
Detach from the screen session:
Now, the server runs in the background even after exiting the session.
Setting Up API Gateway and Implementing CORS
To integrate with AWS API Gateway for better management and usage control, add CORS configuration to FastAPI:
Connect this server to AWS API Gateway to handle authentication and usage management.
Last updated